CASA BLOGS

Importance of Sustainable Management Of Natural Resources
Defining Sustainable Management of Natural Resources
The entire natural world that is beneficial to humans is a resource. Natural resources including soil, minerals, water, coal, forests, and more are truly stocks of these things. But as a result of technological advancement and population growth, our natural resources are being contaminated and depleted.
Sustainable management of natural resources refers to the control of anthropogenic and animal landscape interactions. Planning for land use, protecting biodiversity, managing water resources, and ensuring the long-term success of several businesses, like mining, tourism, agriculture, forestry, and fisheries, are all included. It also acknowledges that people and their means of subsistence depend on the productivity and health of our landscapes, and that sustaining these qualities requires intensive land management. The article examines many sustainable management methods for natural resources.
Key production elements include renewable and non-renewable energy sources, metals and minerals, water, air, biomass, and land. A crucial component of sustainable development is restoring and preserving the health of these resources by embracing resource efficiency. It is required to increase the quality of life for our future generations as well as to feed the current and projected populations. Resource productivity, or the degree to which economic value is added to a given quantity of resources, is measured by useful output or value added per unit of resource input. Resource efficiency, according to UNEP, also includes the technical efficiency of resource use (measured by the useful energy or material output per unit of energy or material input), the degree to which resource extraction or use has a negative impact on the environment, and resource productivity (increased resource efficiency implies reduced the environmental pressures that cause such impacts).
The considerable potential for increased competitiveness and job development serves as a compelling economic justification for resource efficiency. Furthermore, by making more available, the responsible and efficient use of resources and sustainable management will boost social welfare. Additionally, resource efficiency has the ability to enhance waste management, access to food and clean water, and general health. Without necessarily having a negative impact on the economy, resource efficiency can significantly help achieve climate change targets for lowering greenhouse gas emissions. In a recent (May 2016) report, the International Resource Panel, hosted by the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), notes that more effective resource use combined with aggressive climate change action could reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 74% by 2050 while also promoting economic growth. Resource efficiency can have technical, financial, aesthetic, cultural, and other benefits in addition to the beneficial economic, social, and environmental effects.
Pollution
The introduction of pollutants into a substance is referred to as pollution. The term “contaminants” refers to particles that alter physical, chemical, and biological properties in an unfavourable way. Pollution of this kind is most frequently caused by the addition of contaminants to water, soil, and air. Both humans and other Earth’s inhabitants are harmed by this. Therefore, it is urgently necessary to manage and care for the natural resources in order to protect our environment and promote sustainable management of natural resources. International laws, various legislation, and organisations all endeavour to protect our environment. The preservation of the environment and natural resources is a result of people being aware of these issues.
The Ganga Action Plan, as an illustration.
If we use cities as an example, resource efficiency establishes a connection between how cities use and manage the natural resources at their disposal and the quality of life for residents. Resource-efficient cities are able to give livelihood options, notably green jobs, broaden consumer choices, and encourage sustainable lifestyles while combining increased production and innovation with lower prices and fewer environmental impacts. Construction, ecosystem and resource management, renewable energy, and recycling and reusing waste materials, particularly electronic waste, packaging material, plastics, and mineral materials, are some specific economic sectors where green jobs can be produced more frequently. The resilience of ecosystems and their capacity to withstand natural disasters are improved by reducing the overall demand for virgin resources by making better use of the existing stocks of materials present in the urban environment.
Methods of Sustainable Management
Resource efficiency has been given a significant place in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development. Goal 12 on ensuring sustainable consumption and production patterns, in particular in terms of significantly lowering waste generation through prevention, reduction, recycling, and reuse, reflects this in clear words. Goals 2, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14 and 15 are the other eight goals that specifically discuss resource efficiency or sustainable resource usage.
Maintaining economic growth is essential for a nation like India, one of the fastest-growing economies in the world, in order to raise the living conditions of the hundreds of millions of people who are currently living in abject poverty. However, the country’s current development strategy is characterised by a heavy reliance on resource extraction, both domestically and internationally. This puts a tremendous amount of pressure on natural resources, increasing costs, speeding up the rate of forest degradation, and reducing the amount of available agricultural land. The National Environmental Policy was enacted by the Indian government in 2006 with the overarching goals of encouraging intergenerational justice, ensuring the application of sound environmental governance principles, and promoting methods for environmental conservation. However, the Indian industries have not yet sufficiently explored resource efficiency through material-efficient production techniques.
Resource efficiency should be one of the top objectives for enabling sustainable development now and in the future, given the connections between it and the achievement of the SDGs for reducing GHG emissions.
The movement of materials and resources along international supply chains and product life cycles makes it more important than ever to see resources from a global perspective and to integrate different policy areas that support resource efficiency by sustainable management. By adhering to the three R’s of Reduce, Recycle, and Reuse, we may lessen our impact on the environment.
 Previous Blog Post The Ultimate Guide to Disaster Risk Management
Previous Blog Post The Ultimate Guide to Disaster Risk Management 16 days of activism to overcome Gender based Violence
16 days of activism to overcome Gender based ViolenceFeatured Post

Mental Health Awareness in India: Addressing Key Challenges
8 Nov 2024
Mental health awareness is crucial in India, where millions silently struggle with mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and bipolar disorder. Despite growing recognition, India faces unique challenges in effectively addressing mental health issues. The stigma associated with mental illness remains a primary barrier. In Indian society, mental health issues are often misunderstood, leading to […]

Ensuring Girls’ Safety in India: A Path Toward Empowerment
20 Aug 2024
Girls’ safety in India remains a critical issue that has garnered increasing attention over the years. Despite various reforms and efforts from both government and civil society, challenges persist. From street harassment to domestic violence, gender-based discrimination continues to limit the freedom and safety of girls. While significant progress has been made in addressing these […]
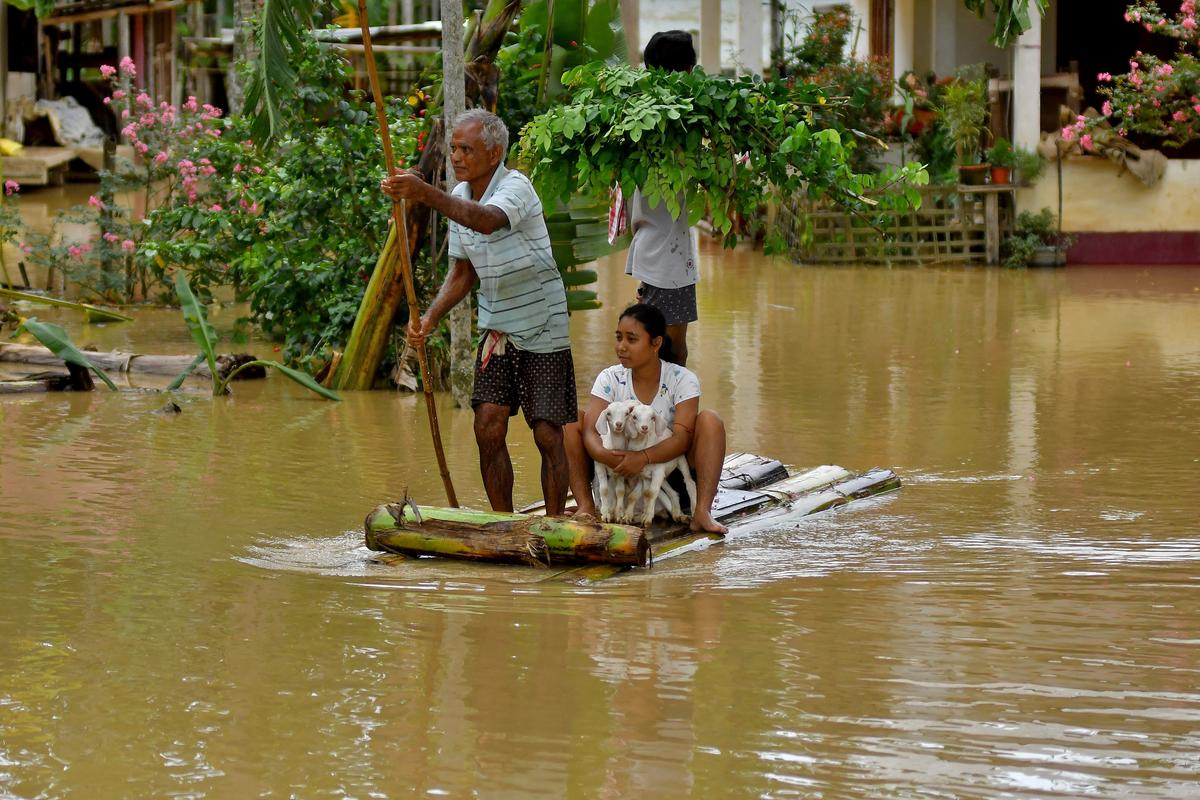

The Connection Between Monsoons and Floods in India: An In-Depth Analysis
9 Jul 2024
India, a land of diverse climates and geographical features, relies heavily on the monsoon season for its agricultural and water resources. However, with the benefits of the monsoon rains come significant challenges, particularly in the form of floods. This blog explores the intricate relationship between the monsoon season and flooding in India, providing detailed insights […]


Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.